Using Cyber Bridge
In this tutorial, we will discuss how to use our Python implementation of cyber brdge implemented in apollo.CyberBridge to communicate with Baidu Apollo. To make this a more hands-on experience, we will programatically reproduce a bug reported in Issue #14551
Step 0: Imports first!
Create a python script at the root directory of DoppelTest and use the following input statements to import the appropriate modules needed for this tutorial
from time import sleep, time
from modules.common.proto.header_pb2 import Header
from modules.common.proto.geometry_pb2 import PointENU
from modules.localization.proto.localization_pb2 import LocalizationEstimate
from modules.routing.proto.routing_pb2 import RoutingRequest, LaneWaypoint
from apollo.ApolloContainer import ApolloContainer
from apollo.CyberBridge import CyberBridge, Topics
Step 1: Initialize Apollo
Starting Apollo, Dreamview, and cyber bridge.
# continued
ctn = ApolloContainer('APOLLO ROOT', 'REPRODUCE')
print('starting docker instance')
ctn.start_instance()
print('starting dreamview')
ctn.start_dreamview()
print('starting cyberRT bridge')
ctn.start_bridge()
print(f'Dreamview at http://{ctn.ip}:{ctn.port}')
At this point, you should expect the following output
Dreamview at https://172.17.0.2:8888
And you can access Dreamview at the URL provided above.
Note
Remember to replace 'APOLLO ROOT' with the actual location of Apollo!
Step 2: Start Required Modules
In order for Apollo to respond to any routing request and make planning decisions to reach its destination, you have to enable 3 modules: Routing, Prediction, and Planning.
# continued
print('starting routing, prediction, planning')
ctn.start_modules()
Step 3: Start up SimControl
SimControl is a feature built-in to Apollo. It is intended to simulate control of the ADS. Upon receiving new planning decisions, SimControl moves the vehicle according to the planned trajectory.
To start SimControl, we have to first publish some localization messages so that SimControl knows where the vehicle is.
# continued
cyber_client = CyberBridge(ctn.ip, ctn.bridge_port)
cyber_client.add_publisher(Topics.Localization)
ctn.dreamview.stop_sim_control()
for i in range(5):
localization_message = LocalizationEstimate()
localization_message.header.sequence_num = i
localization_message.header.module_name = 'Reproduction'
localization_message.header.timestamp_sec = time()
localization_message.pose.position.x = 586952.4339599609
localization_message.pose.position.y = 4141242.6538391113
localization_message.pose.heading = -0.3024105043029949
cyber_client.publish(Topics.Localization, localization_message.SerializeToString())
sleep(0.5)
ctn.dreamview.start_sim_control()
Step 4: Send a routing request
Similar to when publishing localization messages, we can use similar code structure to publish routing request message
cyber_client.add_publisher(Topics.RoutingRequest)
routing_request = RoutingRequest()
routing_request.header.sequence_num = 0
routing_request.header.module_name = 'Reproduction'
routing_request.header.timestamp_sec = time()
routing_request = RoutingRequest(
header=Header(
timestamp_sec=time(),
module_name="Reproduction",
sequence_num=0
),
waypoint=[
LaneWaypoint(
pose=PointENU(
x=586952.4339599609,
y=4141242.6538391113,
),
),
LaneWaypoint(
pose=PointENU(
x=586993.905385346,
y=4141232.039176395
)
)
]
)
sleep(2)
cyber_client.publish(Topics.RoutingRequest, routing_request.SerializeToString())
At this point, you should be able to visualize (in Dreamview) the ADS instance sitting on top of a stop line associated with a stop sign. As discussed in Issue #14551, since Apollo was initialized on top of a stop line, a bug is preventing it from moving forward and leaving this stop-sign-controlled junction.
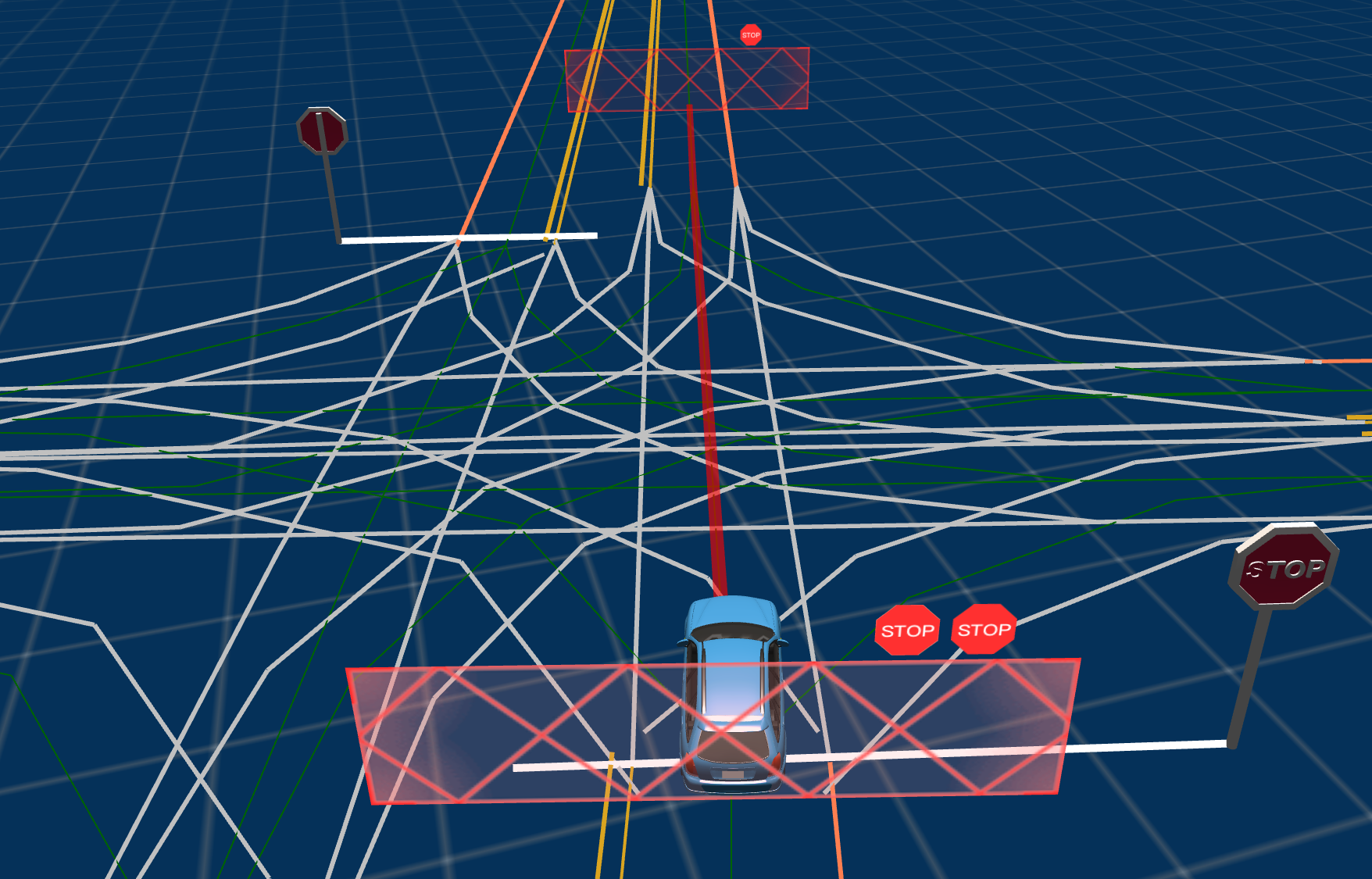
Screenshot of Dreamview when reproducing this bug
Step 5: Same routing request, different initial location
To reproduce the bug, we need to initialize Apollo on top of the stop line and send a routing request to the same destination.
ctn.dreamview.stop_sim_control()
for i in range(5):
localization_message = LocalizationEstimate()
localization_message.header.sequence_num = i
localization_message.header.module_name = 'Reproduction'
localization_message.header.timestamp_sec = time()
localization_message.pose.position.x = 586948.6158271139
localization_message.pose.position.y = 4141243.845017862
localization_message.pose.heading = -0.3024105043029949
cyber_client.publish(Topics.Localization, localization_message.SerializeToString())
sleep(0.5)
ctn.dreamview.start_sim_control()
routing_request = RoutingRequest(
header=Header(
timestamp_sec=time(),
module_name="Reproduction",
sequence_num=0
),
waypoint=[
LaneWaypoint(
pose=PointENU(
x=586948.6158271139,
y=4141243.845017862,
),
),
LaneWaypoint(
pose=PointENU(
x=586993.905385346,
y=4141232.039176395
)
)
]
)
sleep(2)
cyber_client.publish(Topics.RoutingRequest, routing_request.SerializeToString())
At this point, you should be able to observe Apollo moving towards its destination. For the 2 scenairos above, the only difference is where Apollo was initialized at.
Recap: The complete code example
from time import sleep, time
from modules.common.proto.header_pb2 import Header
from modules.common.proto.geometry_pb2 import PointENU
from modules.localization.proto.localization_pb2 import LocalizationEstimate
from modules.routing.proto.routing_pb2 import RoutingRequest, LaneWaypoint
from apollo.ApolloContainer import ApolloContainer
from apollo.CyberBridge import CyberBridge, Topics
# STEP 1
ctn = ApolloContainer('/home/yuqi/ResearchWorkspace/BaiduApollo/D_Apollo_2', 'REPRODUCE')
print('starting docker instance')
ctn.start_instance()
print('starting dreamview')
ctn.start_dreamview()
print('starting cyberRT bridge')
ctn.start_bridge()
print(f'Dreamview at http://{ctn.ip}:{ctn.port}')
# STEP 2
print('starting routing, prediction, planning')
ctn.start_modules()
# STEP 3
cyber_client = CyberBridge(ctn.ip, ctn.bridge_port)
cyber_client.add_publisher(Topics.Localization)
ctn.dreamview.stop_sim_control()
for i in range(5):
localization_message = LocalizationEstimate()
localization_message.header.sequence_num = i
localization_message.header.module_name = 'Reproduction'
localization_message.header.timestamp_sec = time()
localization_message.pose.position.x = 586952.4339599609
localization_message.pose.position.y = 4141242.6538391113
localization_message.pose.heading = -0.3024105043029949
cyber_client.publish(Topics.Localization, localization_message.SerializeToString())
sleep(0.5)
ctn.dreamview.start_sim_control()
# STEP 4
cyber_client.add_publisher(Topics.RoutingRequest)
routing_request = RoutingRequest()
routing_request.header.sequence_num = 0
routing_request.header.module_name = 'Reproduction'
routing_request.header.timestamp_sec = time()
routing_request = RoutingRequest(
header=Header(
timestamp_sec=time(),
module_name="Reproduction",
sequence_num=0
),
waypoint=[
LaneWaypoint(
pose=PointENU(
x=586952.4339599609,
y=4141242.6538391113,
),
),
LaneWaypoint(
pose=PointENU(
x=586993.905385346,
y=4141232.039176395
)
)
]
)
sleep(2)
cyber_client.publish(Topics.RoutingRequest, routing_request.SerializeToString())
print('Observe a stop sign decision is built, but Apollo does not move forward.')
input('Press enter to continue: ')
# STEP 5
print('Moving Apollo away from stop line and sending routing request to the same destination')
ctn.dreamview.stop_sim_control()
for i in range(5):
localization_message = LocalizationEstimate()
localization_message.header.sequence_num = i
localization_message.header.module_name = 'Reproduction'
localization_message.header.timestamp_sec = time()
localization_message.pose.position.x = 586948.6158271139
localization_message.pose.position.y = 4141243.845017862
localization_message.pose.heading = -0.3024105043029949
cyber_client.publish(Topics.Localization, localization_message.SerializeToString())
sleep(0.5)
ctn.dreamview.start_sim_control()
routing_request = RoutingRequest(
header=Header(
timestamp_sec=time(),
module_name="Reproduction",
sequence_num=0
),
waypoint=[
LaneWaypoint(
pose=PointENU(
x=586948.6158271139,
y=4141243.845017862,
),
),
LaneWaypoint(
pose=PointENU(
x=586993.905385346,
y=4141232.039176395
)
)
]
)
sleep(2)
cyber_client.publish(Topics.RoutingRequest, routing_request.SerializeToString())
print('Observe Apollo completes the routing request.')