Pixel-wise Attentional Gating for Scene Parsing
Last update: June 27, 2018.
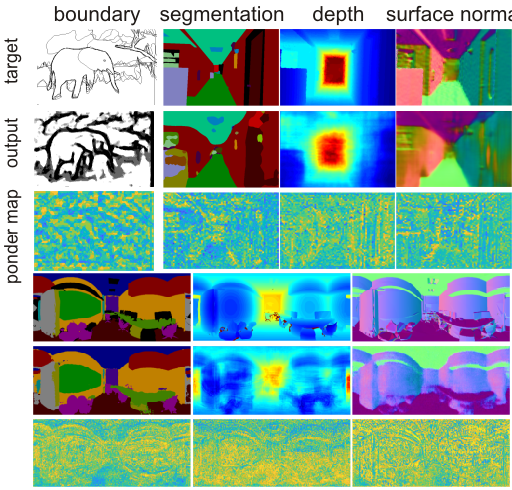
To achieve parsimonious inference in per-pixel labeling tasks with a limited computational budget, we propose a Pixel-wise Attentional Gating unit (PAG) that learns to selectively process a subset of spatial locations at each layer of a deep convolutional network. PAG is a generic, architecture-independent, problem-agnostic mechanism that can be readily ``plugged in'' to an existing model with fine-tuning. We utilize PAG in two ways: 1) learning spatially varying pooling fields that improve model performance without the extra computation cost associated with multi-scale pooling, and 2) learning a dynamic computation policy for each pixel to decrease total computation while maintaining accuracy. We extensively evaluate PAG on a variety of per-pixel labeling tasks, including semantic segmentation, boundary detection, monocular depth and surface normal estimation. We demonstrate that PAG allows competitive or state-of-the-art performance on these tasks. Our experiments show that PAG learns dynamic spatial allocation of computation over the input image which provides better performance trade-offs compared to related approaches (e.g., truncating deep models or dynamically skipping whole layers). Generally, we observe PAG can reduce computation by 10% without noticeable loss in accuracy and performance degrades gracefully when imposing stronger computational constraints.keywords: spatial Attention, Dynamic Computation, Per-Pixel Labeling, Semantic Segmentation, Monocular Depth, Surface Normal, Boundary Detection.
-
S. Kong, C. Fowlkes, "Pixel-wise Attentional Gating for Scene Parsing", WACV, 2019.
[project page] [paper] [github] [slides] [ROB Challenge Entry of Depth] [ROB Challenge Entry of Semantic Segmentation]
![[lng_lat_ecef]](http://www.ics.uci.edu/~skong2/image/PAG_splashFigure.png)